
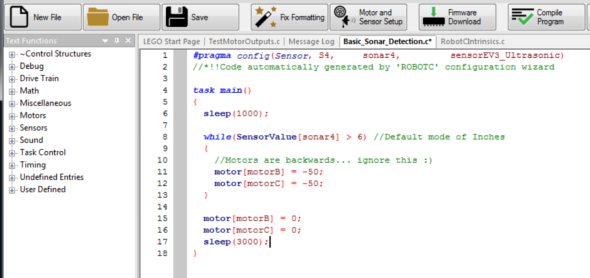
Returns the speed value of the motor plugged into nMotorIndex.Loop until the current encoder counts are equal to the target counts Set the target of motor A to 1000 encoder counts at speed 50 Returns the encoder value of the motor plugged into the port specified by nMotorIndex in degrees.Ĭode Example: //Reset the motor encoder value to zero.Resets the encoder value of the motor plugged into nMotorIndex to 0.Ĭode Example: //Resets the encoder value of motor port A to 0įloat getMotorEncoder ( tMotor nMotorIndex )įunction returns a floating point decimal value.Void resetMotorEncoder ( tMotor nMotorIndex ) RepeatUntil(getMotorEncoder(motorA) = getMotorTarget(motorA)) Set motor A's target of 1000 degrees at speed 50 Note: to return the current encoder position (and not the target position), use the getMotorEncoder command instead.Ĭode Example: //Reset the encoder count of motor A.This command returns the current encoder target value of the motor plugged into nMotorIndex.into port 2 to -2000 degrees at a speed of -75įloat getMotorTarget ( tMotor nMotorIndex )įunctions returns a floating point decimal value. Sets the absolute position target of the motor plugged into motor port A to 1000 degrees at a speed of 50 The resetMotorEncoder(nMotorIndex) command should be used before a moveMotorTarget(nMotorIndex) to ensure the motor is turning in the correct direction.Ĭode Example: //Sets the absolute position target of the motor plugged.nPosition takes values in degrees (unless the encoder units are set to a different mode using the setMotorEncoderUnits command.The set distance to travel specified by nPosition. The port the motor (in servo mode) is plugged into to nMotorIndex. This command needs three pieces of information. This command tells the robot to move an absolute distance.SetMotorTarget(nMotorIndex, nPosition, nSpeed)

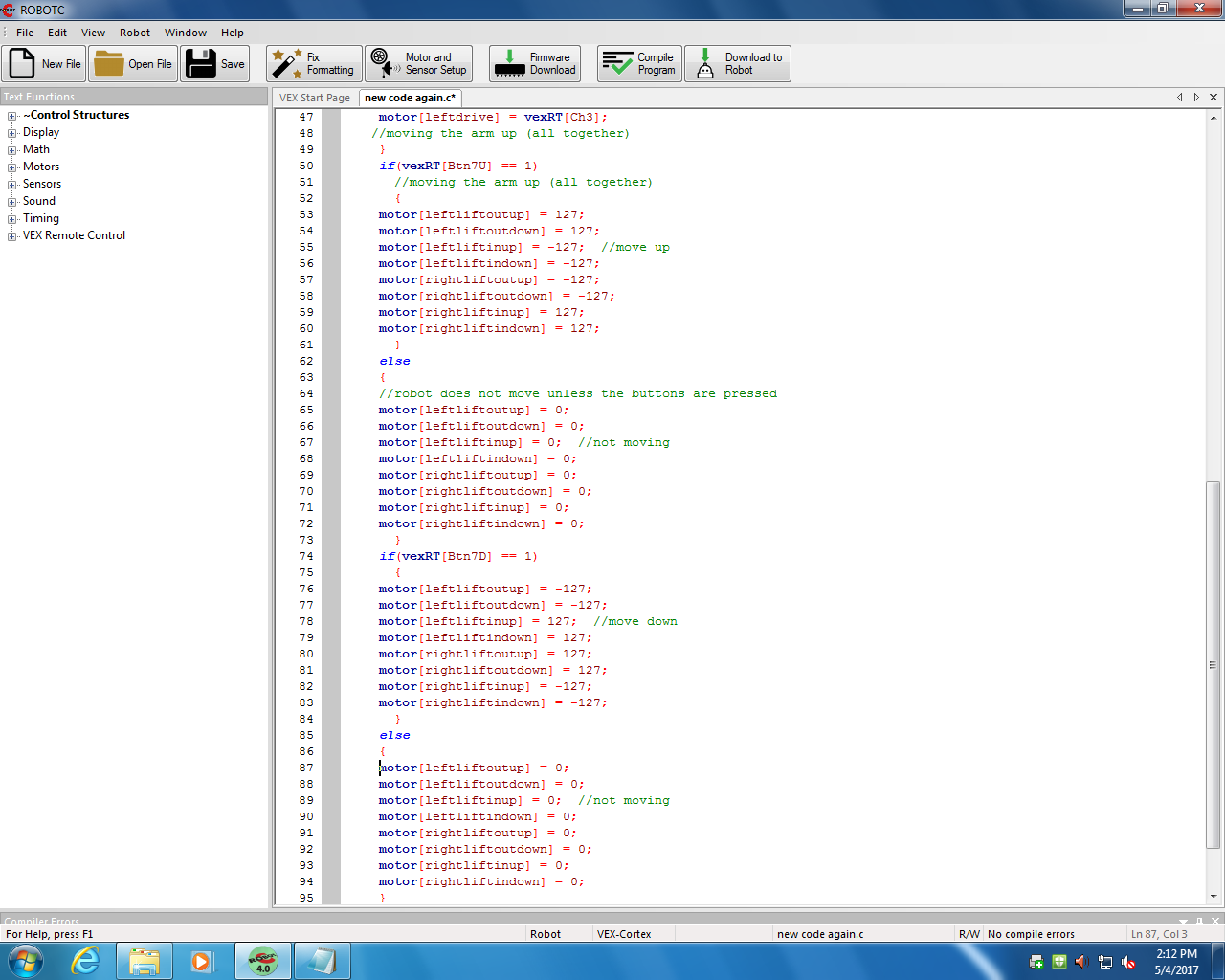
Target absolute value that the motor will travel to. Void setMotorTarget ( tMotor nMotorIndex, float nPosition, int nspeed ) Moves the motor on motorA -1000 encoder counts (backwards) At the end of this command, the motor will automatically come to a stop.Ĭode Example: //Moves the motor on motor port A 1000 degrees (forward).Setting either the target or the speed to a negative number will cause the motor to rotate backwards.The third item is the velocity, which is designated by the nSpeed command.The amount of degrees (incremental), which is designated by nPosition command.The motor, which is designated by the nMotorIndex command.The command needs three pieces of information:
It will add (or subtract) distance from any previously specified targets.

Sets the speed value of motor motor port A to stopped (0)īool waitUntilMotorStop ( tMotor nMotorIndex ) Sets the speed value of motor motor port A to half-speed backwards (-50) Halt program flow for 1000ms (1 second)
#PROGRAMMING IN ROBOTC FULL#
A zero value stops the motor.Ĭode Example: //Sets the speed value of motor motor port A to full forward (+100)
Port number that the motor is plugged into. Void setMotorSpeed ( tMotor nMotorIndex, int nSpeed ) A count of 180 indicates that the motor has traveled half of a rotation. The encoders have 360 counts per single revolution of the motor. Each motor is equipped with an integrated encoder that can be used to determine the current position of the motor. There are four motor ports on the EV3 labeled A, B, C, and D. Our Function Library (Updated Spring 2013) EV3 - Motor Commands


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
